In this section we'll show you how to define a Job.
We'll start with the simple stuff, and then move on to advanced configurations like inter annotator agreement and pre-annotations.
What is a Job
A job in LightTag defines the work that you want done and who should do it. LightTag is in charge of getting the right work to the right person, and automates away most of the project management work for you.
Basic Job
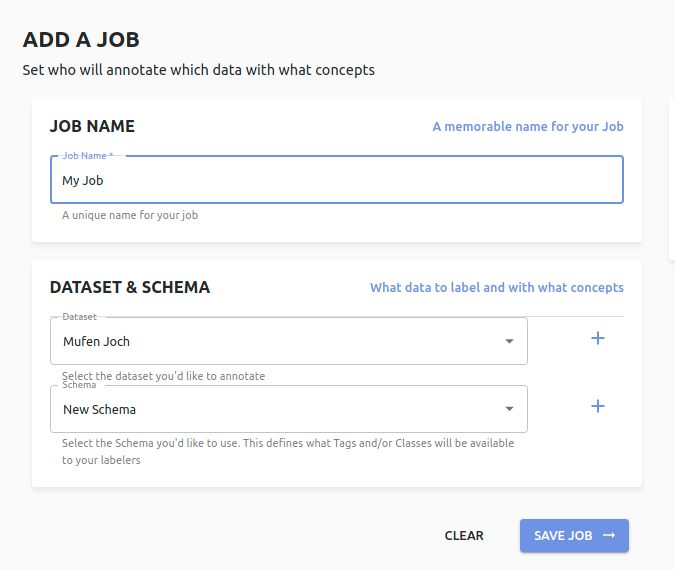
At a minimum, you need to give your Job a name and say which dataset to annotate and with which schema.
Once you do that, the job will be in the work queue.
Prioritizing A New Job
When you add a job, you'll be asked if you'd like to make it top priority.
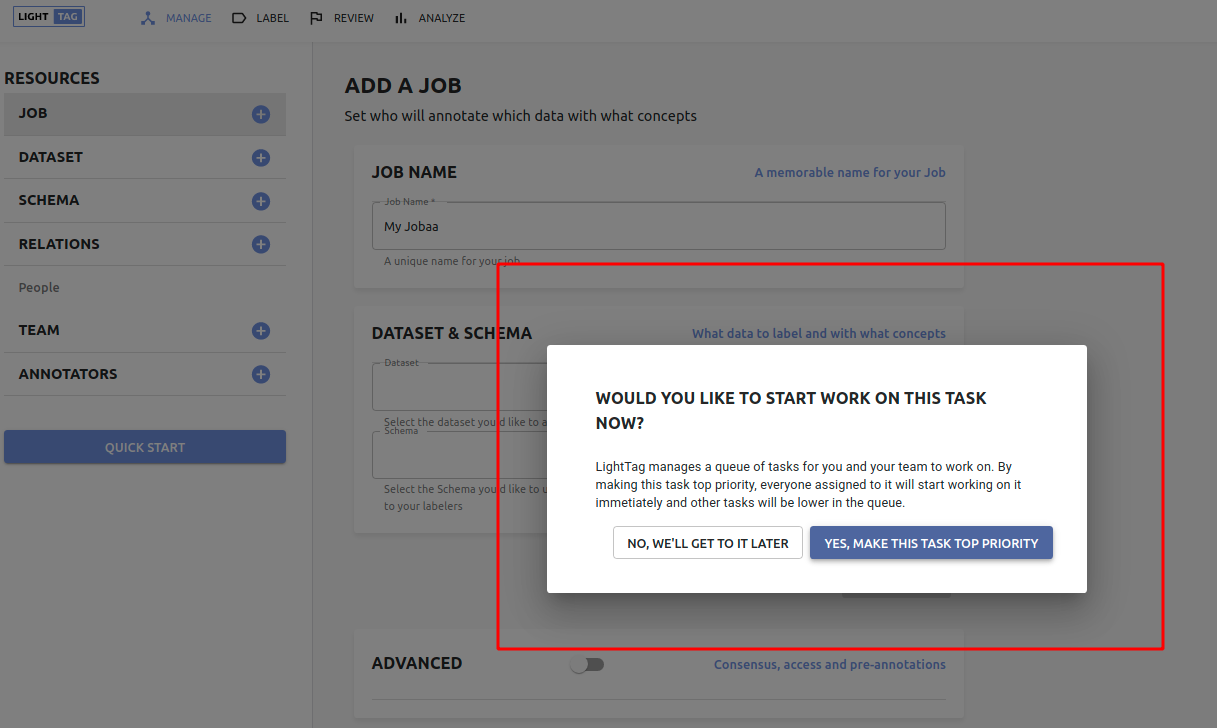
If you do make it top priority, it goes to the top of the Job queue. That means that anyone assigned to the job will start working on it immediately. Otherwise it goes to the bottom of the queue.
Adding Guidelines
Guidelines are instructions you give to your annotators. LightTag will always have them available to your annotators as they work, but you need to write them.
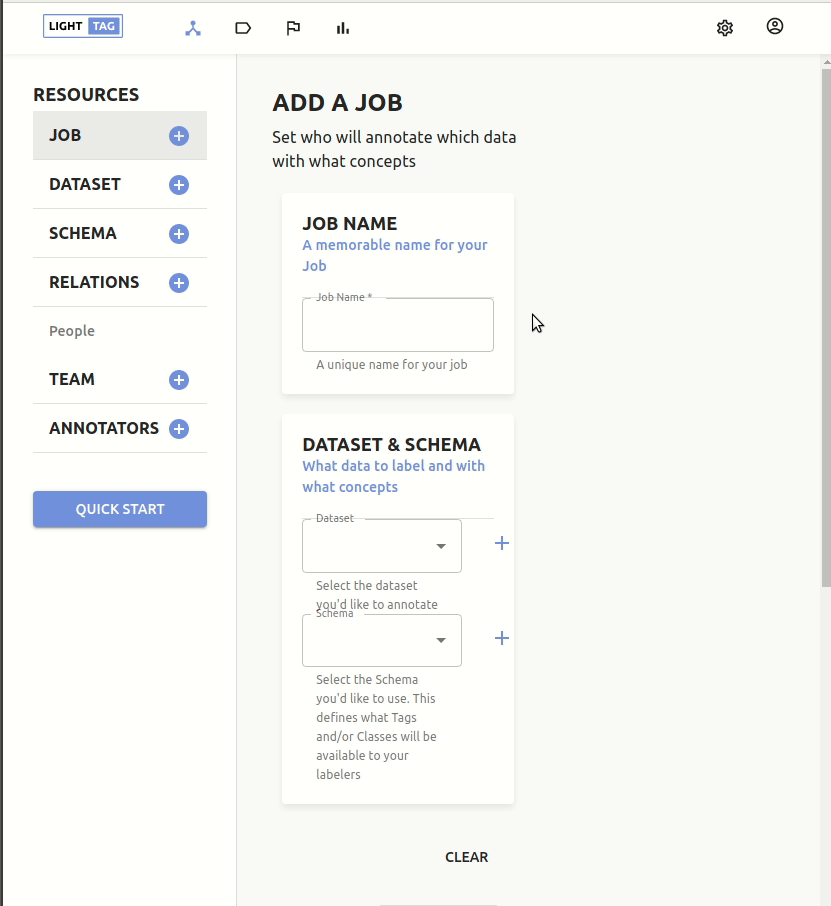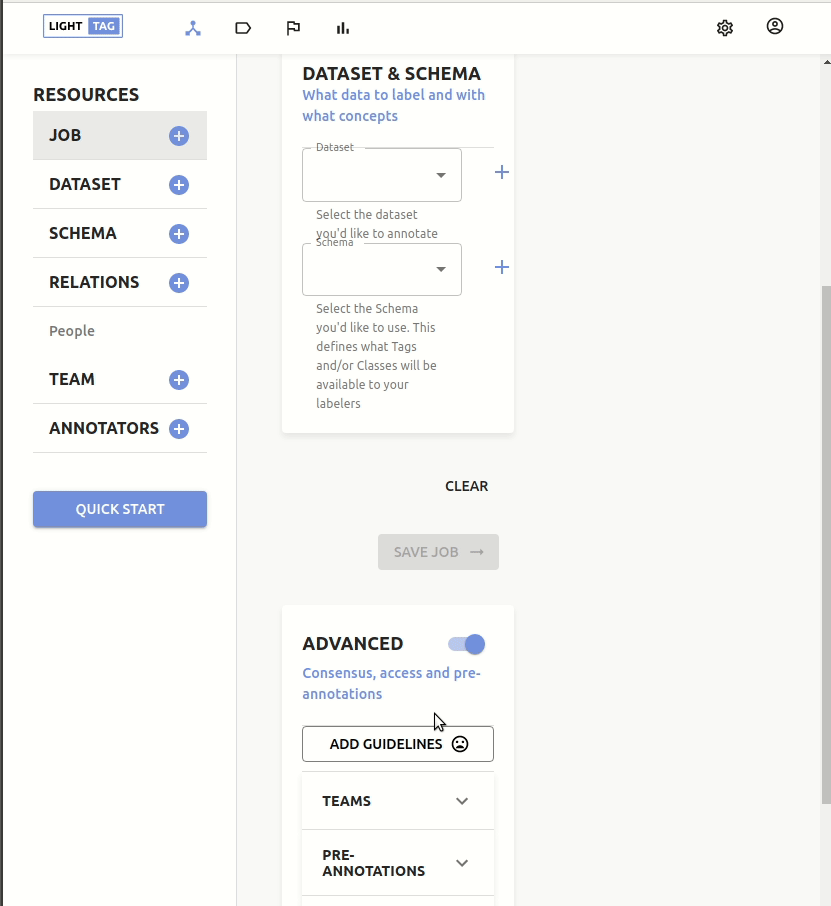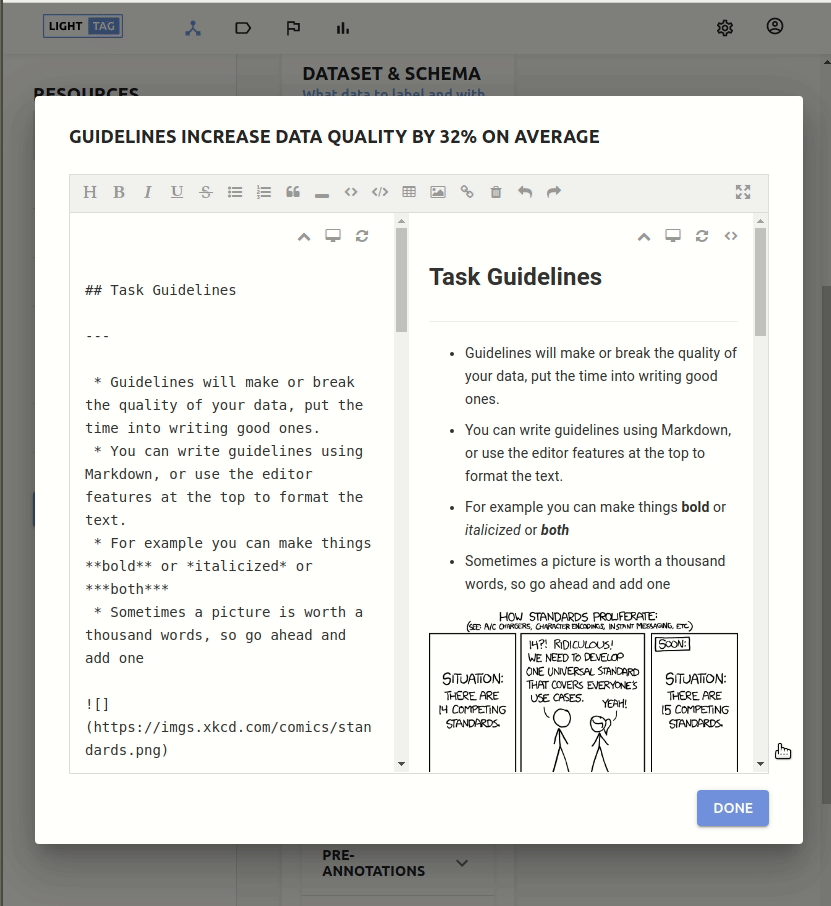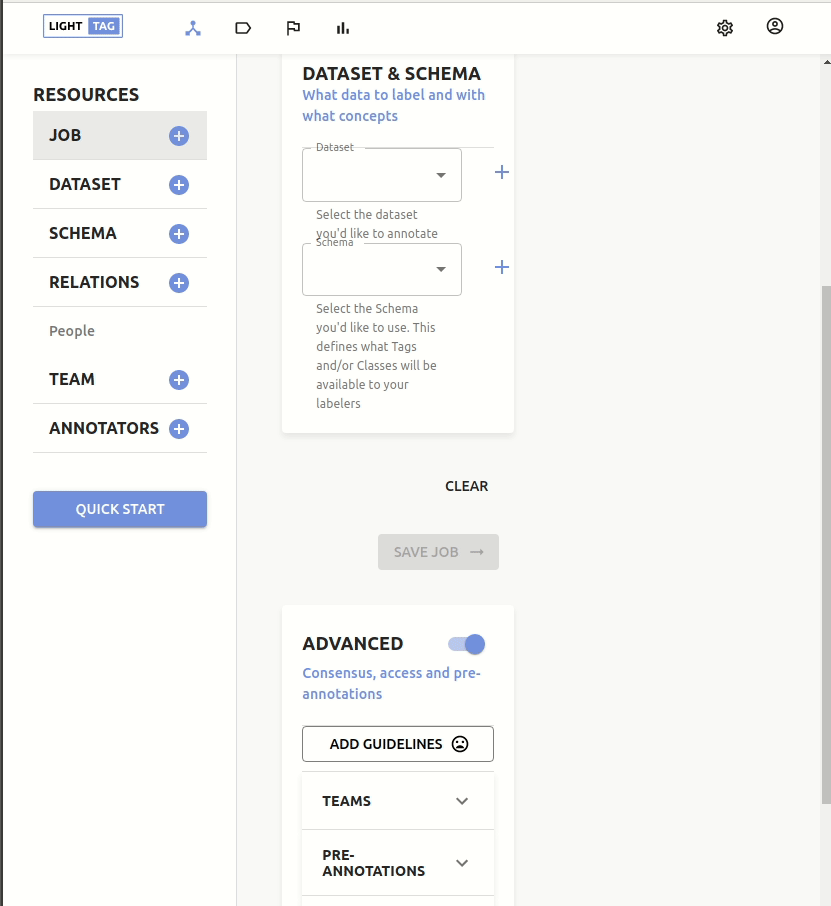
To add guidelines to a new job open the advanced section and click Add Guidelines.
A visual editor will pop up where you can write guidelines, add images and links and tables etc.
Specifying Who Can Work On A Job
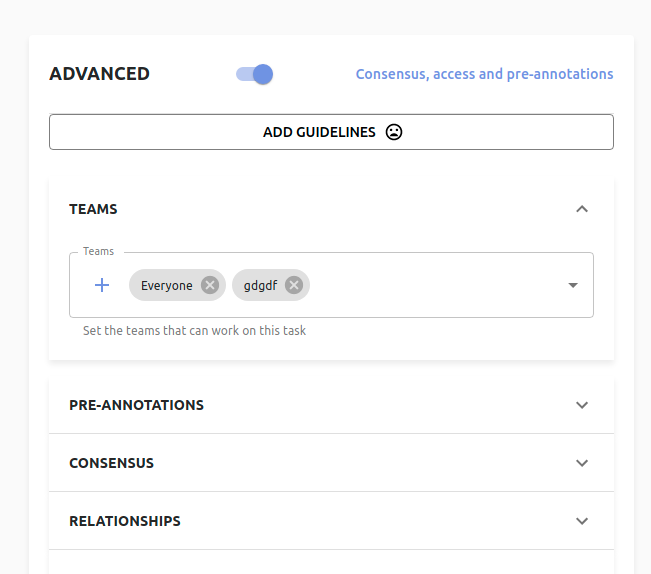
By default your job is assigned to Everyone, but you can assign it to a specific team by toggling the teams section of the advanced field.
Pre-Annotations
By default, LightTag will learn from your annotators and provide suggestions / pre-annotations. You can also upload your own pre-annotations and define the job to use them.
Pre-annotations come from a "model" that you register in LightTag (we register our own for you) and you can select the model(s) that should display pre-annotations for a particular job
Consensus / Inter Annotator Agreement
It's often useful to have multiple people annotate the same example so that you can assess quality. We're big believers in this, it makes labeled data much higher quality and so the default is 3 annotators per example. You can change that to 1 or more.
Relationships
If you'd like your team to annotate with advanced relationship features like Pseudonodes and relation types, you'll choose your relation schema here and it will be part of the job